Projektmanagement@GJW
DE
Planen
Warum: Organisation realistisch auf Ziel ausrichten (im Projektdreieck aus Qualität-Zeit-Kosten Zeit und Kosten beschreiben).
.
Wie: Planen.
.
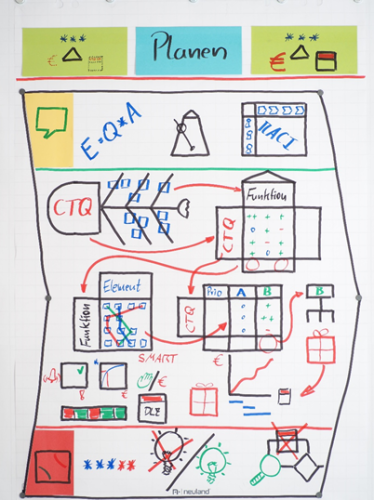
Was: Auf Basis der Design-Score-Card (Input) starte die Phase Planen. Mit z.B. einem Ursachen-Wirkungs-Diagramm können mögliche Funktionen zum realisieren der CTQ gefunden werden. Das zweite Haus der Qualität aus der QFD ermittelt die relevanten Funktionen. In z.B. einem Morphologischen Kasten lassen sich Elemente zu den Funktionen zuordnen und ein Grob-Konzept finden. Die Pugh-Matrix stellt die Grob-Konzepte den CTQ gegenüber und hilft beim Favorisieren. Die Pugh-Matrix liefert die Basis für den PSP (Projekt-Struktur-Plan) und die Kontrolle zur Erfüllung der CTQ.
Top-Down oder Bottom-Up erstellt liefert der PSP auf der untersten Ebene die erforderlichen Arbeitspakete. Die Arbeitspakete sollten SMART formuliert sein. Die Prioritäts-Matrix und das Pareto-Prinzip helfen beim Terminieren , Detaillieren und der Make-Or-Buy-Entscheidung. Bei der Terminierung sollte zwischen Netto-Arbeitszeit und Brutto-Durchlaufzeit (Wartezeiten; Verfügbarkeiten etc.) unterschieden werden. Als Output der Phase Planen liegen die Arbeitspakete mit Zeit und Kosten vor.
In der Kommunikation sollte auf die Akzeptanz für Maßnahmen geachtet werden, von vorherein auf eine Taktung in der Durchführung geplant werden und entsprechend des Kommunikationsplans gearbeitet werden.
Beim Risiko-Management sollte vor allem dem Overengineering und Not-Invented-Here-Syndrom begegnet werden. Tests-Planung sollte Zeit für Korrekturschleifen vorsehen.
EN
Plan
Why: Align the organization realistically with the goal (describe time and cost within the project triangle of Quality-Time-Cost).
.
How: Plan.
.
What: Based on the Design Scorecard (Input), the Planning phase begins. For example, with a Cause-and-Effect Diagram, potential functions to realize the CTQs can be identified. The second house of quality from QFD determines the relevant functions. Elements can be assigned to the functions and a rough concept can be found using techniques like a Morphological Box. The Pugh Matrix compares the rough concepts to the CTQs and helps in prioritization. The Pugh Matrix provides the basis for the PSP (Project Structure Plan) and controls for meeting the CTQs.
Created either in a top-down or bottom-up approach, the PSP provides the necessary work packages at the lowest level. The work packages should be formulated using SMART criteria. The priority matrix and the Pareto principle aid in scheduling, detailing, and the make-or-buy decision. When scheduling, a distinction should be made between net working time and gross lead time (waiting times, availabilities, etc.). The output of the Planning phase consists of work packages with time and cost estimates.
In communication, attention should be paid to the acceptance of measures, a rhythm in execution should be planned from the outset, and work should be carried out according to the communication plan.
In risk management, particular attention should be given to overengineering and the Not-Invented-Here syndrome. Test planning should allocate time for correction loops.
Geplante/Erforderliche Verbesserungen
tbd